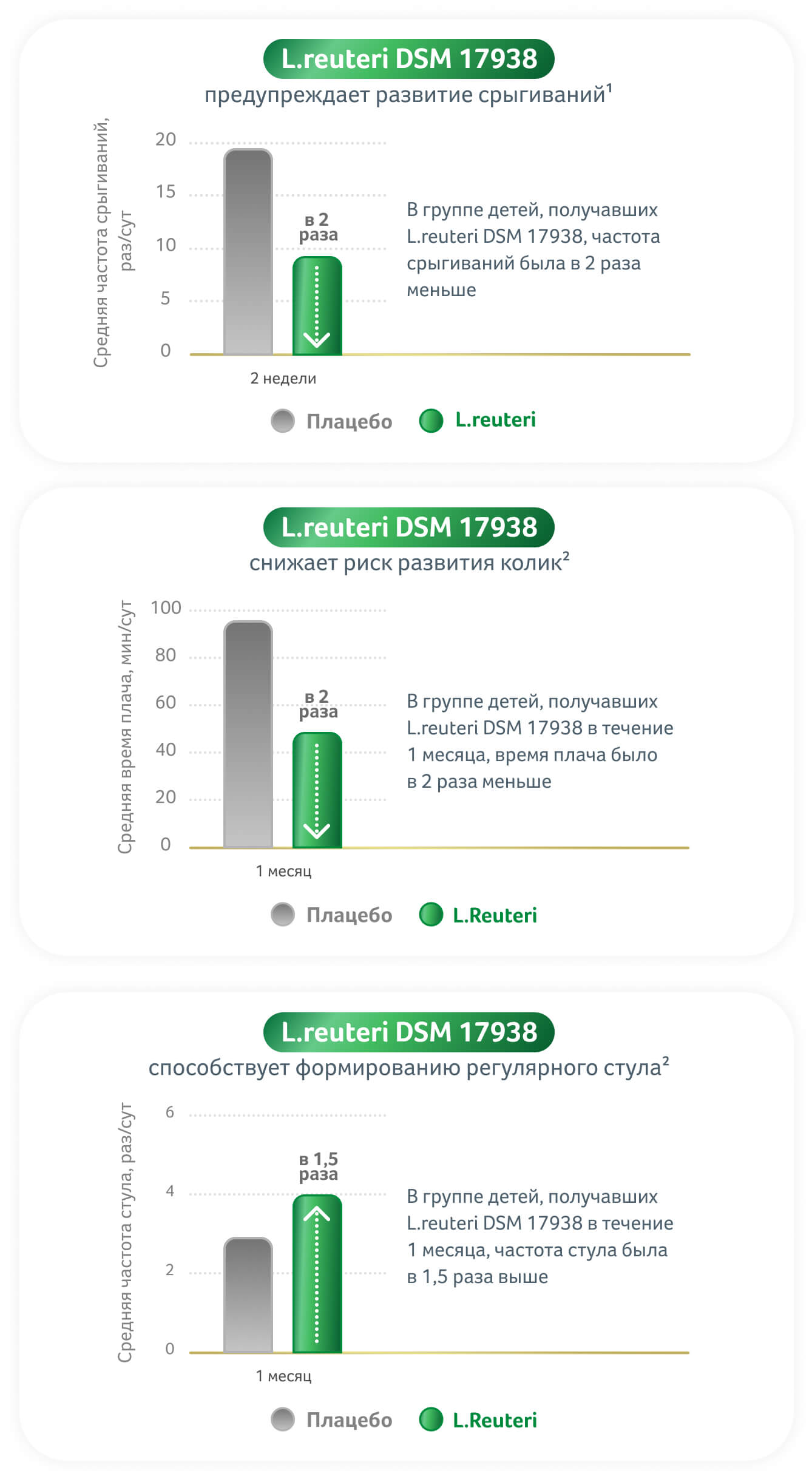
Информация на этом сайте предназначена исключительно для медицинских работников и применима только к продуктам, которые продаются в Российской Федерации. Если вы — медицинский работник, отметьте «Я согласен/согласна» и нажмите «Продолжить», чтобы получить доступ к материалам. Если вы являетесь будущими родителями или родителями и ищете информацию, пожалуйста, перейдите на наш сайт
https://www.nestlebaby.ru.
Важное замечание и заявление
Посещая этот сайт и используя его материалы, вы подтверждаете, что являетесь практикующим медицинским работником. Содержание этого сайта предназначено только для информационных и образовательных целей. Nestlé поддерживает и продвигает рекомендацию Всемирной организации здравоохранения об исключительно грудном вскармливании в первые 6 месяцев с последующим введением полноценного прикорма при продолжении грудного вскармливания до двух лет и более.